Before the Cycle
The physicians at CRM in collaboration with patient coordinators and the rest of the IVF team provide individualized care to optimize treatment outcomes. The IVF cycle start date depends on where the patient is in her menstrual cycle and the IVF cycle protocol (course of medication) prescribed by the physician.
IVF Orientation Class
CRM offers an IVF orientation class. Taught by an IVF nurse, the class includes:
- Staff introduction
- Treatment timeline
- Medication protocols
- How to mix and administer medications
- Injection techniques
- Post-treatment follow-up
- Support services and frequently asked questions
- Billing and insurance questions
After orientation, the patient meets with her IVF nurse to review her specific medication protocol.
IVF orientation classes are generally held Monday through Thursday at 9:30 AM at CRM's Upper East Side office and at other locations by request.
Step-by-Step IVF
Ovarian Stimulation
Suppression Phase
During IVF treatment, some patients may undergo hormone suppression in order to promote a coordinated ovarian response during stimulation. Medications such as birth control pills, estrogen patches, GnRH antagonists (Ganirelix or Cetrotide) or Lupron may be used to suppress the patient’s natural production of endogenous hormones (e.g. FSH and LH).
Stimulation Phase
The purpose of ovarian stimulation is to promote the growth of multiple mature oocytes (eggs).
During the stimulation phase of an IVF cycle, patients self-administer hormones by subcutaneous (under-the-skin) and/or intramuscular injections. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing (LH) hormone are the two most commonly used medications. FSH, LH or the combination of the two stimulate the ovaries to "recruit" multiple follicles, the fluid-filled sacs which contain eggs.
The length of the stimulation phase is approximately two weeks and depends on the patient’s response to the medication regimen. Monitoring via blood tests and ultrasound of the ovaries is performed to track this response.
Monitoring During Ovarian Stimulation
Monitoring occurs on site at one of our Center’s offices. Through near-daily cycle monitoring, CRM physicians adjust the medication protocol as necessary and accurately time the egg retrieval. Ultrasound imaging enables the physician to count and measure the follicles. Blood tests quantify hormonal response to stimulation throughout the patient’s IVF treatment. At each of these visits, signs and symptoms of side effects and any potential complications, such as OHSS, are also assessed.
Upon review of ultrasound and blood test results, the physician will make an informed decision regarding medication dosage and when to return for additional monitoring. Then, the IVF nursing team will notify the patient of the physician’s treatment plan.
Ovulation Trigger
When the follicles are of optimal size, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), Lupron, Ovidrel or Lupron + hCG are administered to initiate the final maturation process of the eggs. The timing and administration of this trigger is of critical importance.
Egg Retrieval
The patient undergoes egg retrieval approximately 34-36 hours after the ovulation trigger. As timing is critical to the success of this procedure, the patient (and partner, if applicable) should arrive at the IVF suite on the 8th floor of NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital at the time specified by the IVF team.
Egg retrieval is a transvaginal surgical procedure lasting approximately fifteen minutes. Using ultrasound to visualize the ovaries, the physician gently removes the eggs and follicular fluid from each follicle using an aspiration needle. Intravenous sedation is administered for the egg retrieval to ensure patient comfort and safety. The post-operative recovery period usually lasts one hour. Some patients experience mild cramping and soreness after the procedure. Other medications such as an antibiotic may also be prescribed during this time.
Sperm Preparation
Depending on patient-specific circumstances, CRM's IVF team will require a fresh and/or frozen sperm samples to be available on the day of egg retrieval.
Fresh Specimen
The male partner generally produces a fresh semen specimen at the Embryology Laboratory, on the day of the retrieval procedure. Embryology Laboratory staff process the specimen before using it to fertilize the retrieved eggs.
Frozen Specimen
Patients may also use frozen sperm specimens, either partner or donor, for fertilization.
Partner Frozen Specimen
Prior to the female partner commencing treatment, the partner will communicate with the patient coordinator to schedule an appointment for semen analysis and cryopreservation.
Anonymous Donor Specimen
While CRM is not a sperm bank, our patients routinely use frozen anonymous donor sperm specimens transported from New York State-accredited banks in ovulation induction or in vitro fertilization cycles. CRM's Andrology Laboratory staff schedules the receiving and preparation of donor sperm with the patient.
As most banks require three business days to ship samples, patients are encouraged to have their samples shipped to the Andrology Laboratory prior to the treatment cycle.
Please contact the Andrology Lab at (646) 962-8448 with any questions. Please note that we are generally unable to use specimens from banks that are not accredited by New York State.
Directed Donor Specimen
A directed sperm donor is someone who is known to the recipient, but is not her sexually intimate partner. There are multiple regulatory requirements that must be met for the use of directed donor sperm. Patients must speak with their CRM Physician in order to ensure the proper coordination and timing throughout treatment.
Fertilization
Retrieved eggs are fertilized either by conventional insemination, the placement of eggs and sperm in a culture-containing dish, or by intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) by the embryologists and andrologists in CRM’s Embryology Laboratory. For more information about ICSI, visit the technique’s page. Embryos (successfully fertilized eggs) are closely watched by the embryologists as their cells begin to divide using the latest Embryoscope technology.
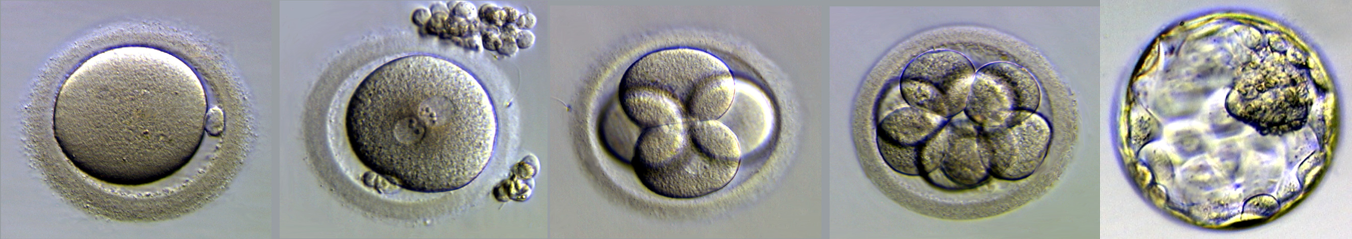
Above: Images of embryo development.
Fertilization Results
Patients will be contacted on the day following retrieval with the number of eggs retrieved and fertilization results if applicable. The number of eggs retrieved varies substantially depending on a number of factors, including but not limited to the patient’s age and response to the stimulation medications. The number of eggs retrieved does not directly correlate to IVF success because egg quality can vary.
Progesterone Supplementation
Progesterone is a hormone that supports the growth of the endometrium, the lining of the uterus, in order to create a healthy environment for a transferred embryo to implant. IVF patients typically begin progesterone supplementation the day after egg retrieval. Progesterone stimulates the receptivity of the lining of the uterus for embryo implantation. Progesterone supplementation is not required for patients freezing eggs or embryos.
Embryo Transfer
Embryologists monitor the embryos’ growth and viability and carefully consider patient-specific factors to determine whether a day 3 or day 5 transfer is appropriate. Embryo transfers performed three days after retrieval (day 3 transfers) involve the placement of cleavage stage embryos (four-to-eight cells) into the uterus. Alternately, in a day 5 transfer the embryo has typically achieved the blastocyst stage of development at the time of transfer. Our Center has seen excellent pregnancy rates with both day-3 and day-5 transfers. The clinical decision on whether to proceed with a day 3 or day 5 transfer is made by the physician and embryology staff after thoughtful consideration of all treatment options.
Embryo transfer is an outpatient procedure that typically does not require anesthesia and is performed at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital. Using a catheter, a physician places the embryo(s) selected for transfer into the patient’s uterus via the cervix. The number of embryos transferred is decided by the physician and patient prior to the procedure based on the patient's specific clinical history.
Embryo Cryopreservation
After the embryo transfer, the embryologist evaluates any remaining embryos for cryopreservation (freezing). Embryo cryopreservation gives patients who wish to have another child the option to have an embryo transferred at a later date without having to complete another IVF cycle.
After Transfer
Two weeks after retrieval, a pregnancy blood test is performed. If this test is positive, the patient is considered four weeks pregnant and pregnancy hormone levels will be further monitored by blood testing. Patients with successful cycles will follow up with their CRM physician for an ultrasound, after which they will transition to an obstetrician’s care.


